Ainda sem produtos na sua encomenda!
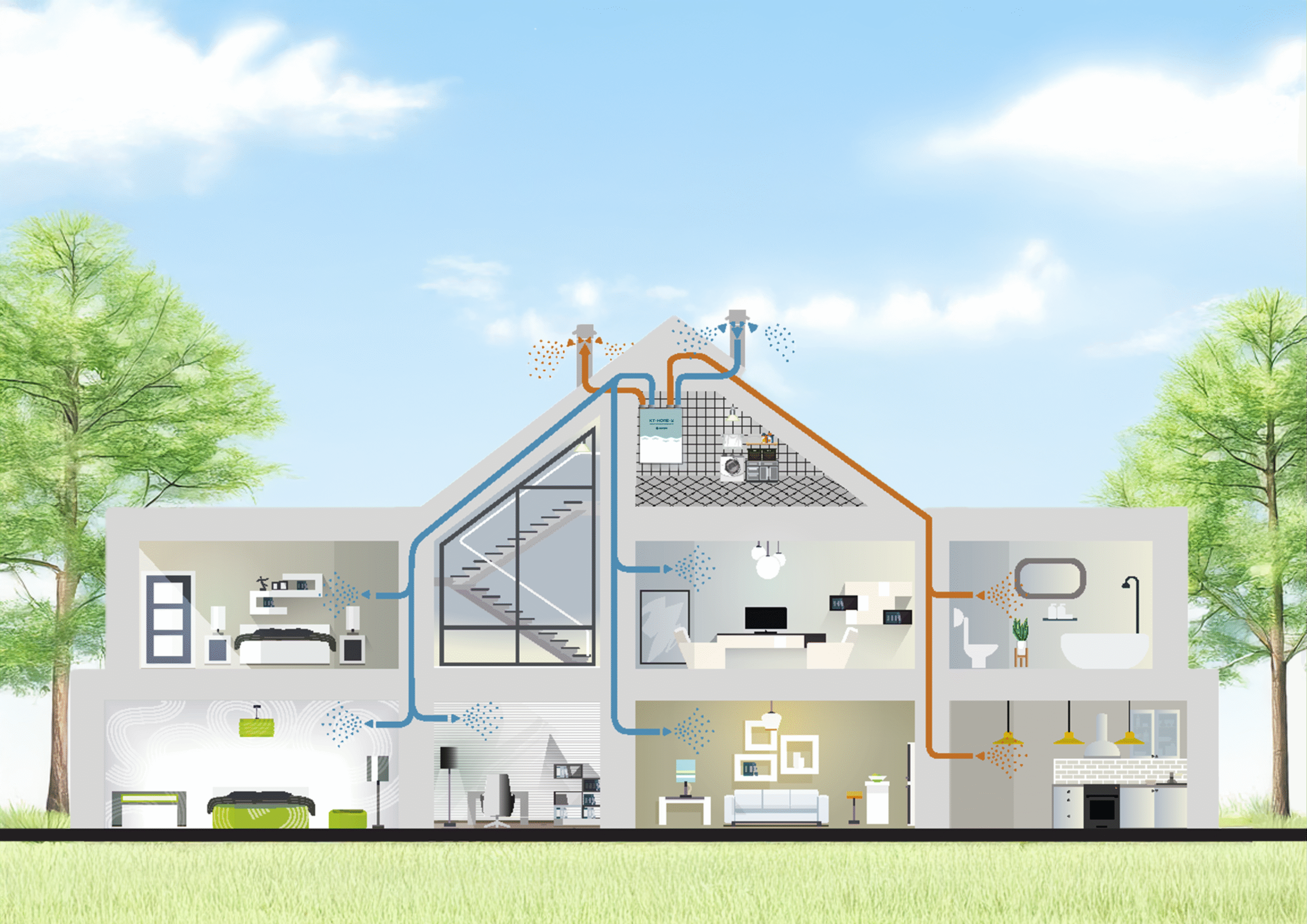
Energy efficiency has become a priority in all human activity, and reducing our ecological footprint is imperative. At the same time, Indoor Air Quality (IAQ) is increasingly valued, not only for its influence on health and well-being, but also on the productivity of those who occupy modern buildings, from homes to offices, schools, hospitals and industrial environments.
Historically, buildings had few windows and low airtightness. In single-flow CMV systems, air was only extracted, and new air entered through window gaps or passive ventilation grilles. Today, buildings are much more insulated and brighter, an evolution that requires controlled and balanced ventilation.
This is where the dual-flow CMV system with heat recovery comes in, which not only removes polluted air, but also treats it and brings the temperature of the supplied air closer to that of the return air, combining energy efficiency, thermal comfort and clean air.
Controlled Mechanical Ventilation is a system that ensures continuous and controlled renewal of indoor air.
While natural ventilation is unpredictable, CMV maintains constant air flows, improving energy efficiency and indoor air quality.
There are two main types of CMV:
Single-Flow systems work only by extracting stale air (kitchens, bathrooms, laundry rooms). Fresh air enters uncontrolled through cracks, windows, or intake grilles.
Although they are a more economical solution in the short term, they have several limitations:
The Double-Flow CMV extracts stale air and blows new, treated and filtered air into the main rooms.
Between these two flows there is a heat exchanger that transfers up to 93% of the thermal energy from the extracted air to the new air.
The result is efficient and balanced ventilation, with several advantages:
In addition, modern dual-flow units can include free cooling and free heating, using outside air to naturally cool or heat the building without additional energy consumption.
The difference between the two systems translates into significant differences in energy consumption and operating costs.
The following simulations show the monthly energy consumption and cost associated with air conditioning, considering a flow rate of 1000m³/h operating 8 hours/day and a setpoint of 20ºC, but with two different configurations:
Monthly graph of energy consumption and air conditioning costs, considering a heat recovery unit with 85% efficiency and electrical heater to cover the remainder if necessary.
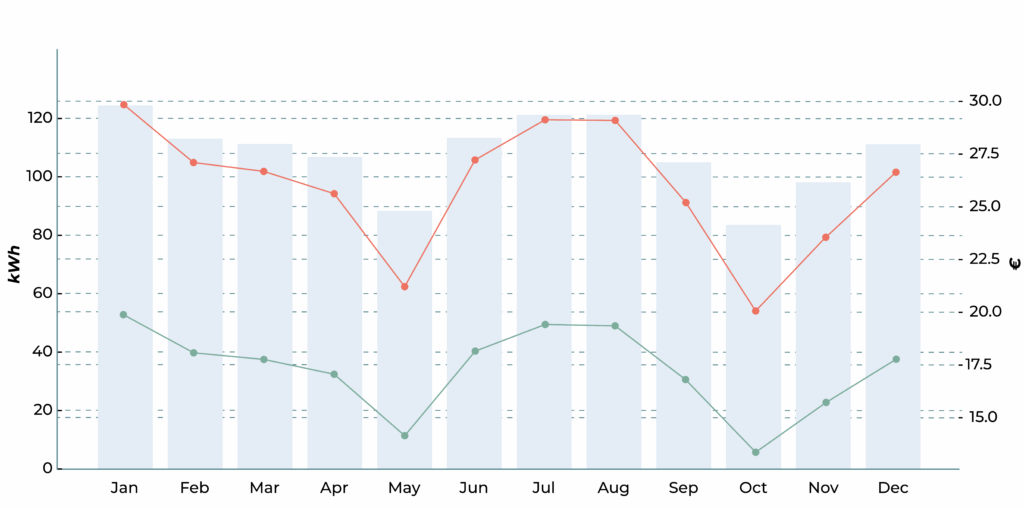
The bars represent total consumption (kWh) per month.
The green line indicates the energy cost at €0.16/kWh.
The red line indicates the energy cost at €0.24/kWh.
The result shows a significant reduction in energy consumption and costs during the cold months, proving the efficiency of heat recovery in heating and cooling fresh air.
Monthly graph of air conditioning consumption and cost, considering a single-direction unit and a DX coil with outdoor unit.
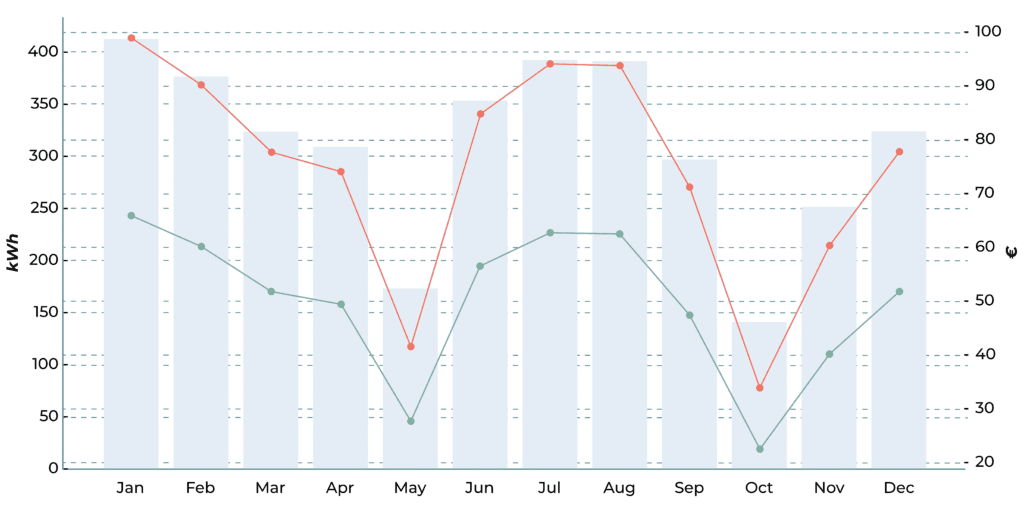
The bars represent total consumption (kWh) per month.
The green line indicates the energy cost at €0.16/kWh.
The red line indicates the energy cost at €0.24/kWh.
In this scenario, energy consumption is considerably higher, especially during winter and summer, due to the absence of heat recovery; the air is heated or cooled entirely using electrical or refrigeration energy.
The difference between the two systems is significant:
These results confirm that investing in double-flow ventilation with heat recovery means investing in the efficiency, sustainability and durability of the building.
Dual-flow CMV systems are not only notable for their energy efficiency, they are also crucial for indoor air quality (IAQ) and, consequently, for the health and comfort of those who live or work in the building.
By ensuring continuous and balanced ventilation, these systems keep the air constantly refreshed, eliminating pollutants, humidity and excess carbon dioxide (CO₂). The result is a healthier, more stable and productive indoor environment.
Controlled mechanical ventilation provides:
Heat recovery ventilation is a versatile solution that can be adapted to different types of buildings, from the residential sector to industrial environments.
In all cases, the objective is the same: to ensure clean air, thermal comfort, and energy efficiency.
OCRAMclima® develops dual-flow controlled mechanical ventilation solutions with heat recovery, designed for efficiency, durability, and comfort.
The KT Home and KT Pro ranges have been designed to meet different needs, from residential spaces to buildings with higher air flow, with simple installation and optimised maintenance.
Heat recovery ventilation is one of the cornerstones of energy efficiency and indoor air quality in modern buildings.
With double-flow technology, it is possible to save energy, improve comfort and ensure a healthier and more sustainable indoor environment.
Explore OCRAMclima® solutions and discover how KT heat recovery systems can optimise energy performance and air quality.