Ainda sem produtos na sua encomenda!
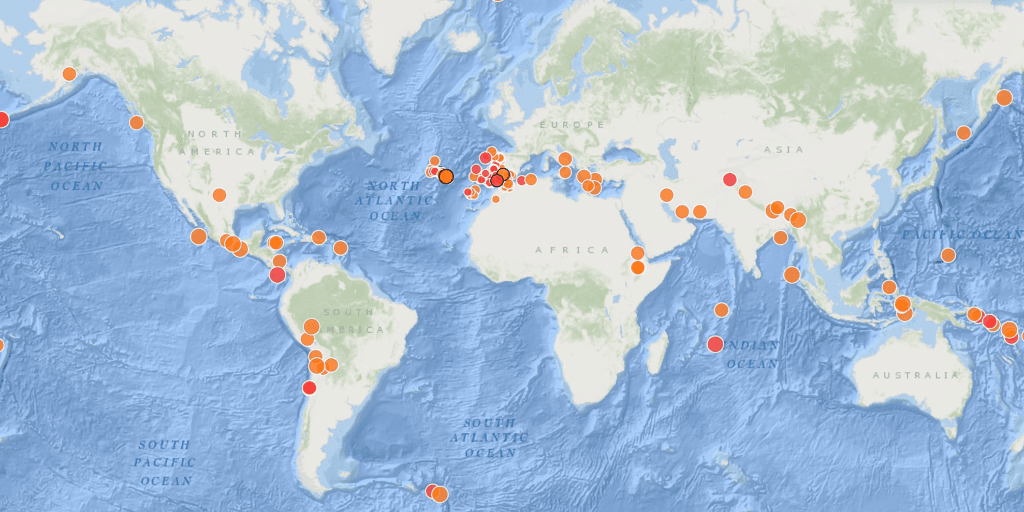
Seismic zones are regions where earthquakes are more frequent, and where accurate cartographic recording is crucial for developing social and urban planning, as well as for adopting risk mitigation measures.
Earthquakes primarily result from the release of energy in the tension zones between tectonic plates (interplate earthquakes). Another cause is volcanic activity and molten material inside the plates (intraplate earthquakes), which, although the seismic magnitude is typically not as high, can have significant consequences due to the epicenter being closer to populated areas.
The main seismic zones of the planet are:
Portugal and Spain have shown some seismic activity, making them higher-risk zones than most of Europe. According to the Portuguese Society of Seismic Engineering, Portugal, particularly in the southern part of the country and the Azores, is characterized as a zone of significant seismicity due to its location. The region is affected by not only interplate earthquakes but also due to the proximity of the following active faults:
In areas prone to earthquakes and tremors, proper design and engineering are essential to ensure the stability of buildings. However, earthquakes can affect not only the structure but also non-structural components, such as mechanical, electrical systems, plumbing, and fire protection systems.
When such an event occurs, the main financial impacts are the costs of equipment repair, cleaning the damage, and the loss of the building’s function.
Especially in an industrial building, replacing HVAC equipment, ducts, pipes, electrical systems, and fire network systems can be more expensive than the structure itself, and damaged non-structural elements can make the building unusable.
The ASCE (American Society of Civil Engineers) has building codes and provides guidelines for the seismic protection of non-structural elements through the Minimum Design Loads for Buildings and Other Structures (ASCE 7, 2010 edition).
The ASCE also assigns importance factors to different equipment. In simple terms, the importance factor reflects the severity of a potential failure of the equipment in question. HVAC equipment, smoke removal systems, backup generators in hospitals, and pipes that transport hazardous materials would all have higher importance factors.
The primary purpose of seismic support is to restrict the horizontal shaking of an earthquake. All seismic supports firmly anchor the equipment to the structural elements of a building, allowing them to move with the structure during an earthquake. This prevents the equipment from tipping over, falling from its suspended location, or colliding with other objects.
Seismic Air Handling Units (AHUs) are essential in earthquake-prone areas as they ensure the continuity of HVAC and ventilation systems, minimizing structural and operational risks.
These structural reinforcement and isolation strategies help ensure that the AHU continues to operate or can be quickly restored after a seismic event, maintaining safety and contributing to the environment’s functionality.
Data centers are the backbone of the digital era, and despite already consuming more than 1% of global electricity, the path to sustainability is set.
With the rise of cloud computing, artificial intelligence, and the Internet of Things (IoT), the demand for data processing and storage is growing at an unprecedented rate. However, this massive expansion brings significant challenges: energy consumption, efficient cooling, environmental impact, and adequate infrastructure.
Reducing energy consumption and the environmental impact of data centers are crucial challenges in the digital age. Regarding energy efficiency, several strategies can help mitigate this situation.
Technology is advancing, but it is up to us to ensure that this evolution is sustainable. The path to more efficient data centers is already laid out—those who follow it will not only reduce costs but also lead the transformation toward a greener and more responsible future.
Discover our suggestions for ensuring efficiency and security in Data Centers:
More about Data Centers:
The data center market in Europe has seen significant growth in recent years and projections indicate that this trend will continue. In 2024, the European data center market was expected to reach 12,23 thousand MW, with an annual growth rate of 7.96%, thus reaching more than 17,93 thousand MW by 2029.
It is estimated that there are over 8,000 data centers worldwide, the largest cluster being in Northern Virginia with over 300 data centers and an energy consumption capacity of 2,552MW.
Portugal, despite being pointed out as a hub and gateway to the world in terms of interconnection, has 35 data centers, although more investment in this sector is planned.
In Europe, the UK is the country with the biggest environmental footprint. The data centers operating out of London require 1,053 MW. On the same list, the second European city with the most installed capacity is Frankfurt, with 864 MW.
Globally, the second region with the most computing capacity is Beijing, with 1,799 MW, which remains the only Asian city to need more than 1,000 MW to power its data centers. The data centers already installed in Tokyo, for example, consume 865 MW.
This growth is driven by several factors, including the increased use of data, the growing demand for cloud computing services and the need for robust e-commerce systems. In addition, the expansion of emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI) and edge computing is contributing to increasingly advanced data center infrastructures.
However, this growth brings with it significant challenges, especially with regard to energy consumption. According to the European Commission, data centers in Europe used 259 TWh of electricity by 2020, representing 1.7% of the world’s total energy consumption. With the market expected to generate 30 times more data over the next ten years, a corresponding increase in energy consumption is expected. Consequently, there is an increasing focus on reducing energy consumption, consolidating wide area networks (WAN) and bandwidth requirements, creating opportunities for the data center interconnection market.
Known as ‘the new vaults’ because they house servers and storage systems, data centers are physical infrastructures designed to store, process and distribute large volumes of data and digital applications. They support the IT operations of companies, governments and internet service providers.
Due to the high energy consumption and environmental impact, there is an increasing focus on the energy efficiency and sustainability of data centers, including the use of renewable sources and advanced cooling technologies.
The future of data centers in Europe looks promising, with continued growth driven by digitalisation and the adoption of new technologies. However, it will be crucial to address the challenges related to energy consumption and sustainability to ensure a balanced and responsible development of the sector.